The Trading Bible Trading Guides Bid and Ask in Trading - Differences Explained
What is Bid and Ask in Trading?
By Stefano Treviso, Updated on: Apr 07 2023.
The Bid is the maximum price at which buyers are willing to buy an asset, the Ask is the minimum price at which sellers are willing to sell an asset and the Spread is the difference between both Bid and Ask prices.
When you see any trading chart and read that the price of a stock is $119.5, you may be not looking at the Bid or Ask price. If you execute a market order you could end up getting a completely different price as the price in the chart could have been the current bid price, the current ask price, a medium of both or the price of the last transaction executed.
It is extremely important in any trading platform to set your charts to look at the specific price you care about, either the bid or the ask.

Some trading platforms will allow you to view the bid and ask in several ways, for example:
- An indicator at the right end of the chart showing the current bid and ask prices
- Using separate lines for the bid and ask all over the chart. This gives you a good idea of how much the spread was changing by looking at how far away the bid and ask lines are throughout the chart
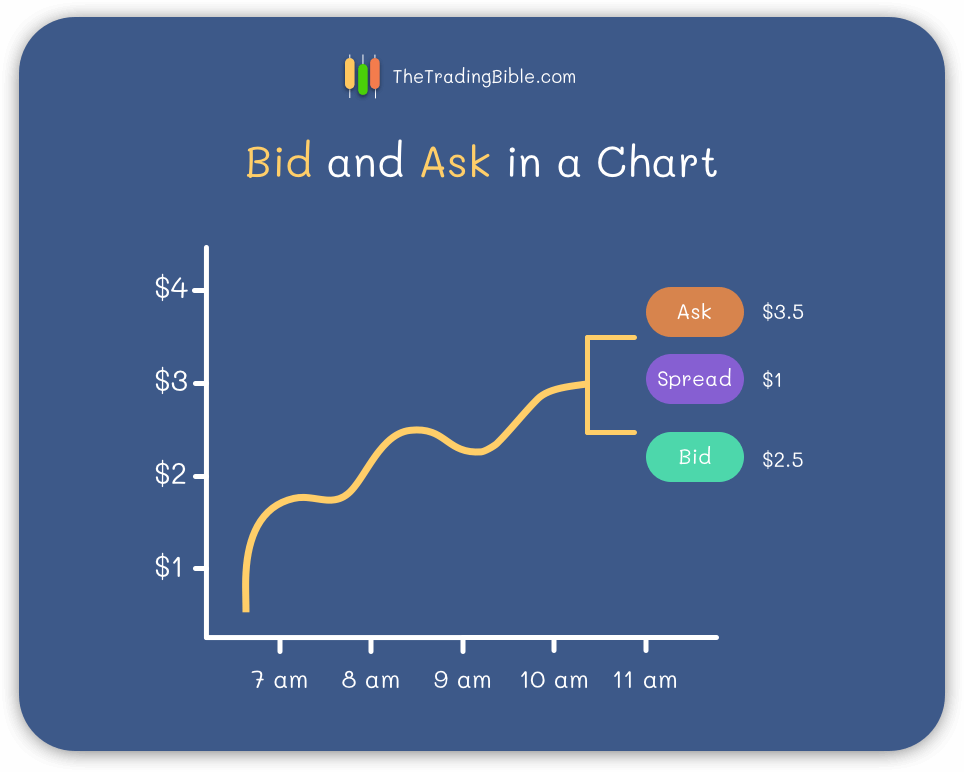
Understanding the Spread
The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices. Market makers set the spread as their compensation for the risk of constantly fulfilling incoming buy and sell orders to maintain market prices, for example: a market maker could have just fulfilled your buy order and immediately the price jumps a few cents causing them a loss.
That's why the spread gets created and you're always buying at a more expensive price or selling at a lower price, this is how market makers profit from providing liquidity (availability of an asset).
Imagine for a second that we want to initiate the market for a particular asset, let's say a stock.
The moment we launch our IPO (initial public offering) and start throwing stocks into the market for traders to buy, we have a problem.
There is no flow in both directions that can maintain a steady price as it's just us selling stocks and people buying, so how can we create a market for a stock from scratch?
We need a lot of traders buying and selling constantly for the market to stabilize and that's when market makers come into play.
Market makers are there to constantly buy or sell the stock to maintain the market price and let the natural forces of supply and demand take place and determine prices over time.
All of this works at a very nice profit for market makers as what they do in simple words is marking up prices at a fee (the spread) in exchange for providing liquidity. Here's how they do it:
- When you buy, you do so at the ask price (more expensive for you)
- When you sell, you do so at the bid price (cheaper for you, which means worst in this case)
As soon as the market is made and there is a lot of participants trading or maybe even other market makers competing to offer their services, there is so much liquidity that the risk of holding that asset and fulfiling orders becomes lower and this causes spreads to become narrower. All of this means that:
- A narrow spread equals to a liquid market (less risk for market makers)
- A wide spread equals to an illiquid or volatile market (higher risk for market makers)
Featured Brokers for Beginners
| Broker | Top Features |
|---|---|
| |
| |
|
Spread on CFD Market Makers
Bear in mind that we just described the market making process for standard securities, in the particular case of CFDs there are some differences:
CFD brokers that hedge their transactions (meaning that they take the underlying position of your trade in the real market) are also subject to the same market spreads which they pass on to you.
Those spreads can be narrowed or widened on purpose by your CFD broker if they choose to do so as their risk management tool to fulfill your CFD orders.
A good example of this can be: the spread on the market can be $0.1 and your CFD broker is giving you a spread of $0.5. This is not necessarily bad as maybe the CFD broker is taking the risk to fulfill an order that you sent that wouldn't have been possible to fill in the real market as there was no liquidity, they're taking the risk to fulfill you.
Why do spreads widen?
Spreads widen due to lack of liquidity and the last one happens due to major price swings, limit orders being removed and market participants not submitting market orders. This causes market makers during their competitive battle for pricing to also widen their spreads to mitigate the risk of a loss while fulfilling orders.
Important things to remember
- Your charts may be set to show bid, ask, medium or last price, be sure to check which one is it
- Market makers set spreads as their compensation for the risk of fulfilling buy or sell orders at all times
- You're always buying at the ask price and selling at the bid price, that's why your trades open in minus, you already paid the spread and you're starting behind
- Spreads are narrow when there is a lot of liquidity and market participants competing to provide the best price
- Spreads widen when there is a lack of liquidity which can be caused by volatility
Good luck and happy trading!


