The Trading Bible Blog ᑕ❶ᑐ TWAP - What Is Time-Weighted Average Price
TWAP Meaning in Trading
By Stelian Olar, Updated on: Nov 22 2025.
In the fast-paced world of financial markets, effectively executing trades, especially a large order, presents a significant challenge. Dumping a massive buy or sell order onto the market at once can trigger adverse price movements, leading to higher costs and missed opportunities. This is where sophisticated execution strategies come into play. One such widely adopted method is the TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price).
This article will delve into what is TWAP, explore the TWAP meaning, its advantages and disadvantages, and compare it with another popular execution algorithm, VWAP, to help you understand its role in modern TWAP trading and minimizing market impact.
So, what is a time-weighted average price?
See below…
What Is Time-Weighted Average Price
At its core, the Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) is an algorithmic trading execution strategy designed to break down a single large order into smaller, more manageable pieces. These smaller orders are then systematically placed into the market at regular time intervals over a pre-defined set period of time.
This is often referred to as the execution horizon or time period.
The fundamental idea behind the time-weighted average price is to spread the execution evenly throughout this time period, aiming to achieve an average filled price that is close to the average market price observed during that duration.
The "time-weighted" aspect is crucial here. A TWAP algorithm differs from volume-weighted strategies. It gives equal importance to each segment of time. This happens regardless of the trading volume within those segments.
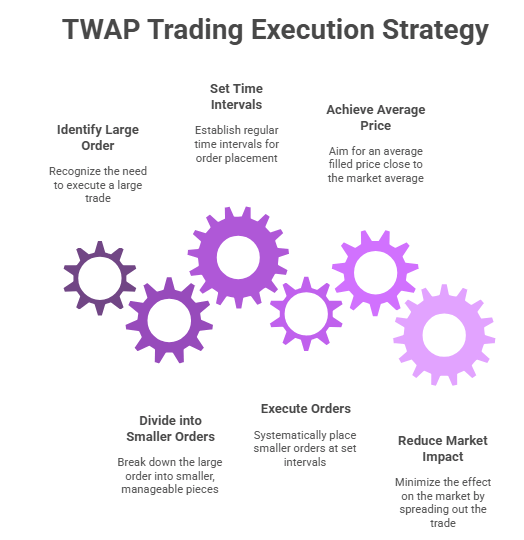
For instance, imagine you want to execute a TWAP order over one hour. The twap algo will divide that hour. It might use sixty one-minute time intervals, or another chosen granularity. Then, the algo will attempt to execute 1/60th of your total order size in each of those minutes.
This systematic approach helps in achieving what is known as the time-weighted mean price.
Understanding what is a time weighted average in this context means recognizing its primary goal: to reduce the impact on the market. By not revealing the full order size at once and by participating consistently over time, a TWAP trade aims for stealth and efficiency. The time-weighted average formula averages execution prices. It gives equal weight to the price of each small portion of the order. This equal weighting applies as each portion is filled across all the time slices. Detailed TWAP calculations confirm this "time-weighting." It comes from the equal distribution of the order quantity over pre-defined time segments.
This is a common order type. Institutional traders often use it. Retail traders with access to advanced platforms also use it more frequently. Understanding what is TWAP trading is essential. It helps anyone looking to manage larger positions effectively.
Advantages of TWAP
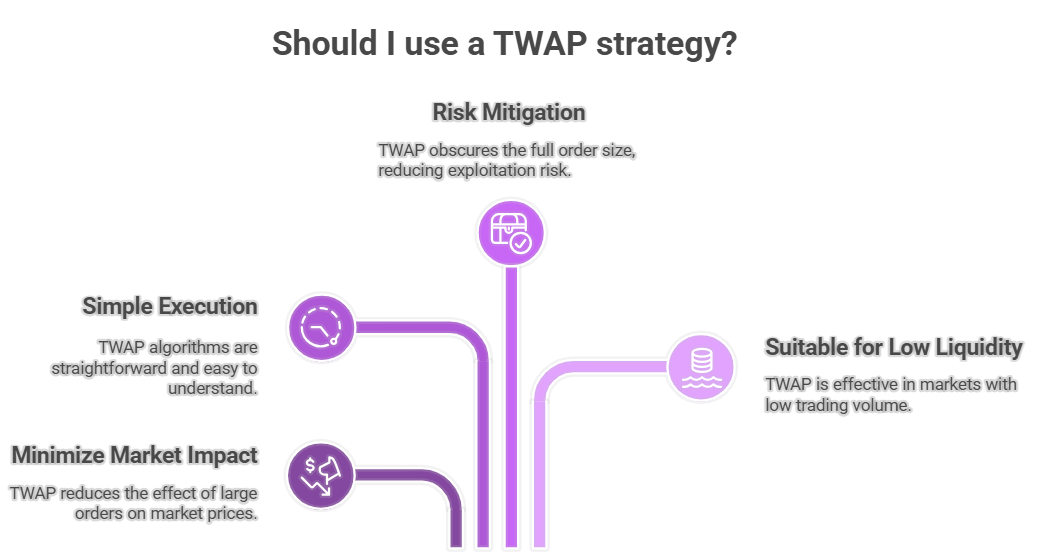
A key advantage of a TWAP strategy is its prowess in minimizing market impact in both traditional markets and TWAP crypto trading. By breaking a large order into smaller segments executed gradually over a set period or time period, it achieves a more favorable average price point with minimal market disturbance. The TWAP algorithm is refreshingly simple; this TWAP algo divides the order by time, offering predictable execution. This method also curtails the risk of being exploited, as the full scale of the TWAP trade is obscured.
A TWAP order is particularly beneficial for discreet trading or in low liquidity scenarios, focusing on consistent participation over the time spent to reduce its impact on the market. This careful execution defines what is TWAP trading.
Disadvantages of TWAP
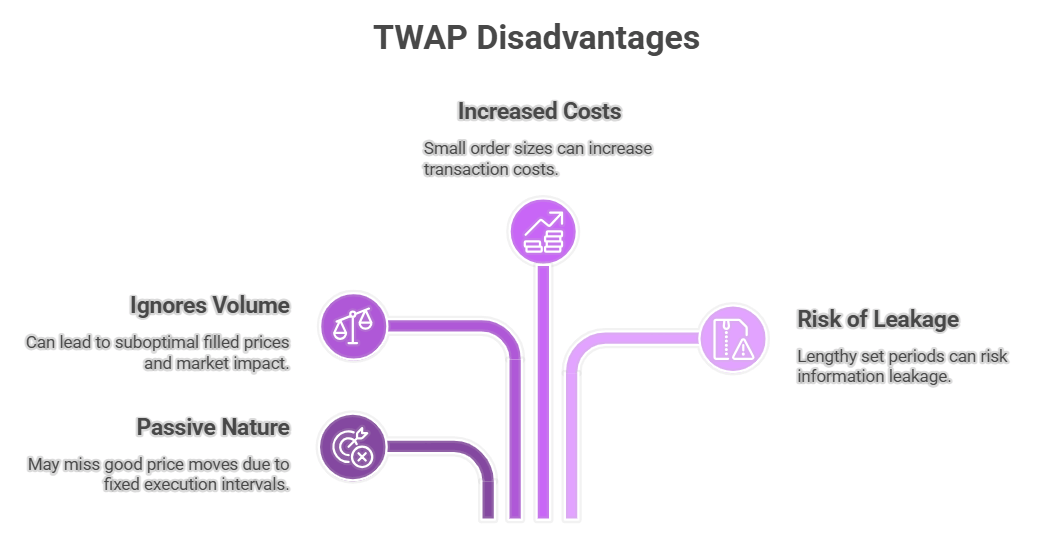
However, a TWAP strategy has disadvantages. Its passive nature is one. This means a TWAP order might miss good price moves during its execution time period. It continues to buy or sell based on time spent, not current market conditions.
The TWAP algorithm also ignores total volume. This can create an undue impact on the market. It might also lead to a suboptimal filled price. This happens because it executes at fixed time intervals, no matter the market's liquidity.
The small order size of each slice from a large order in a TWAP trade is good for overall impact. However, this can sometimes increase transaction costs.
A lengthy set period for the TWAP algo can also risk information leakage. This strategy isn’t ideal if speed is more important than achieving an average price point. The final weighted average price TWAP, which comes from TWAP calculations, is just an average. It is not necessarily the optimal price.
TWAP vs VWAP - Which Is Better
When discussing algorithmic execution strategies for large order fulfillment, the conversation invariably turns to TWAP vs VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price). Both are designed for minimizing market impact and achieving a fair weighted average price, but they approach this goal differently, leading to distinct use cases. Understanding the nuances of VWAP vs TWAP is key to selecting the appropriate order type.
VWAP, or Volume-Weighted Average Price, calculates the average price of an asset. This calculation considers both price and the total volume traded at each price point. It does this over a specific time period. VWAP strategies aim to execute orders at or near this volume-weighted average. They often increase participation when trading volume is higher. They decrease participation when the volume is lower.
The fundamental difference in TWAP calculations versus VWAP calculations lies in their primary driver:
- TWAP: Divides the order size based on fixed time intervals. Each slice of the order is typically of equal size and executed at regular intervals, irrespective of trading volume during those intervals. The focus is on the time spent.
- VWAP: Divides or targets execution based on the asset's historical or real-time volume profile. It aims to execute more of the order when market liquidity (volume) is higher and less when it's lower.
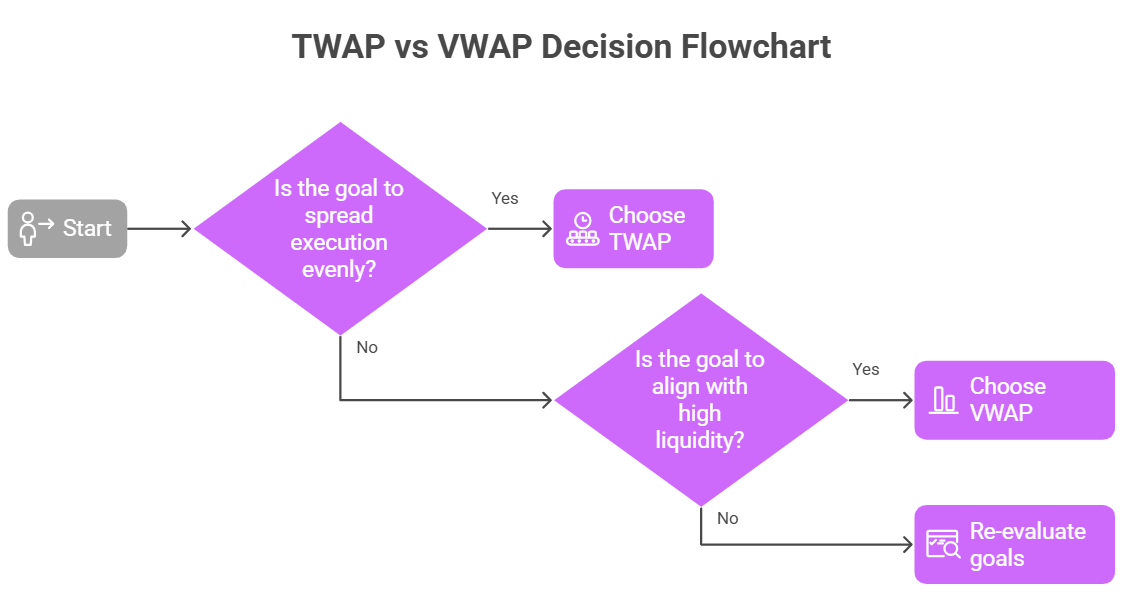
So, which is better when comparing TWAP vs VWAP? There's no universal answer; the optimal choice depends heavily on the trader's objectives, market conditions, and the specific characteristics of the asset being traded.
Choose TWAP when:
- The primary goal is to spread execution evenly over a set period, regardless of volume fluctuations.
- You want to minimize the risk of "chasing volume" or being overly influenced by short-term volume spikes that might not be sustainable.
- Dealing with assets where volume data might be less reliable or susceptible to manipulation.
- A consistent, predictable participation rate over time is desired for executing trades.
- The TWAP meaning in crypto context often favors TWAP due to erratic volume profiles in some digital assets.
Choose VWAP when:
- The goal is to align execution with periods of higher market liquidity. This approach can lead to tighter bid-ask spreads. It also means less impact per share traded during these high-volume moments.
- You want the execution benchmarked against where the bulk of the day's trading activity occurred.
- There's a belief that participating more heavily during high-volume periods will result in a more "representative" filled price.
- Trading for less liquid coins: understanding what is TWAP in crypto involves applying this time-slicing to manage risk in volatile digital asset markets.
Both TWAP and VWAP are effective tools. They help manage the execution of a large order. Their goal is to achieve a weighted average price TWAP or VWAP, respectively.
The decision in the VWAP vs TWAP debate often depends on a trader's priority. Some prioritize time-based execution with TWAP. Others prefer volume-based participation with VWAP. Institutional traders might use hybrid strategies. They may also switch between TWAP and VWAP as market conditions change.
Understanding their mechanics is key. You need to grasp what is time weighted average. It's also vital to see how it differs from volume weighting. This knowledge helps you make an informed decision. The right choice should suit your specific trading scenario.
Ready to apply your knowledge of TWAP? Discover how forex brokers like Pepperstone, FP Markets, and Deriv can provide the tools you need to manage your TWAP orders and aim for your desired time weighted average price.


