The Trading Bible Blog ᑕ❶ᑐ Quant Trading: Definition, Meaning, Examples
What Is Quantitative Trading in Finance
By Stelian Olar, Updated on: Aug 08 2025.
So, what is quant trading, really?
Quantitative trading, or quant trading, is a special way to trade in markets. It doesn't use gut feelings or old-style company reviews. Instead, it uses trading strategies based on quantitative analysis. This involves using math and statistics. It means crunching numbers to find good trading opportunities. Key data inputs like price and volume are frequently fed into these mathematical models to guide buy and sell decisions.
In the past, mostly large firms and hedge funds used these methods. Now, better technology and data access make quantitative trading tools available to more individual traders.
So, what is quantitative trading fundamentally? It's about building and executing trading strategies based on objective, historical data and math. The goal is to take emotion out of the decision-making process. This article explains the quantitative trading meaning. It also covers examples, typical strategies, what a quant trader does, career paths, and how it differs from algorithmic trading. Think of this as an introduction to quantitative trading.
Now that we know the quantitative trading definition, let’s see some examples…
Examples of Quantitative Trading in Action
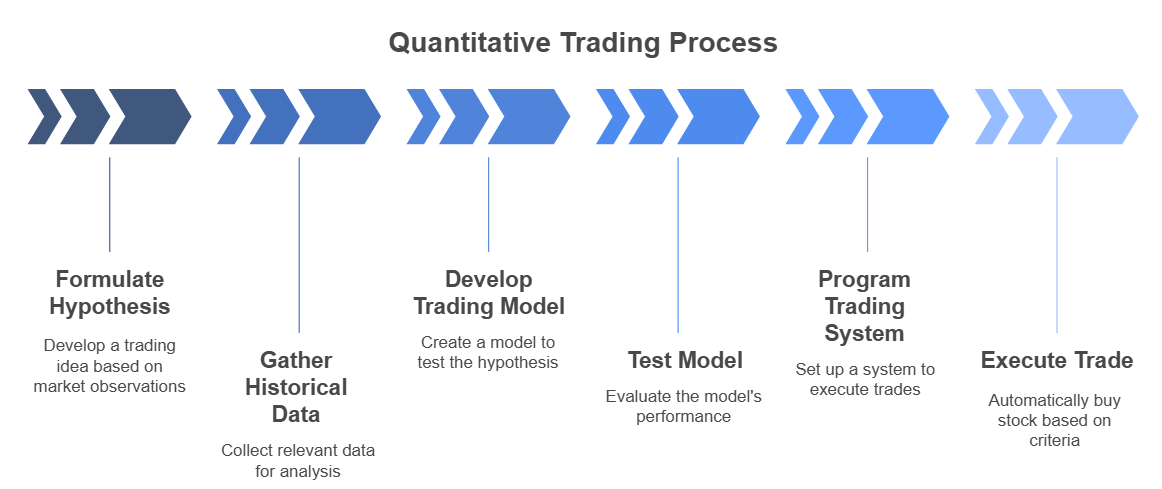
Let's consider a practical example to understand what quantitative trading is in action. A quant trader might believe that a stock goes up after a company reports earnings that beat analysts' expectations. But it usually depends on one thing - the trading volume must also be unusually high during the announcement.
A quantitative trader wouldn't just act on this hunch. They would:
- They collect past data. This includes data on earnings announcements, analyst expectations, and price movements. It also includes how prices changed and trade volumes.
- Develop a quantitative trading model using statistical methods to test this hypothesis rigorously. Does the upward drift reliably occur? How strong is the pattern? Does the high volume condition actually improve the outcome?
- If the statistical models confirm a profitable pattern with acceptable risk, they would program a system. This system watches for earnings news. It checks if the results are good enough and if the volume is high enough. If so, it automatically makes a quant trade to buy the stock. The system then holds the stock for a set time.
Another common example is pairs trading, a form of statistical arbitrage. A quant trader might notice that two stocks in the same sector (say, two large banks) usually move in tandem. Their quantitative trading model tracks the price ratio or spread between these two stocks. If this spread gap gets too wide, the model acts. It might buy the cheaper stock and sell the pricier one. The bet is that the gap will return to normal.
The choice to buy and sell depends only on this statistical difference. It's not based on the banks' fundamental analysis. Crypto quantitative trading uses similar ideas for digital assets. It looks at blockchain data or exchange orders to find patterns for crypto quant trading.
Quantitative Trading Strategies
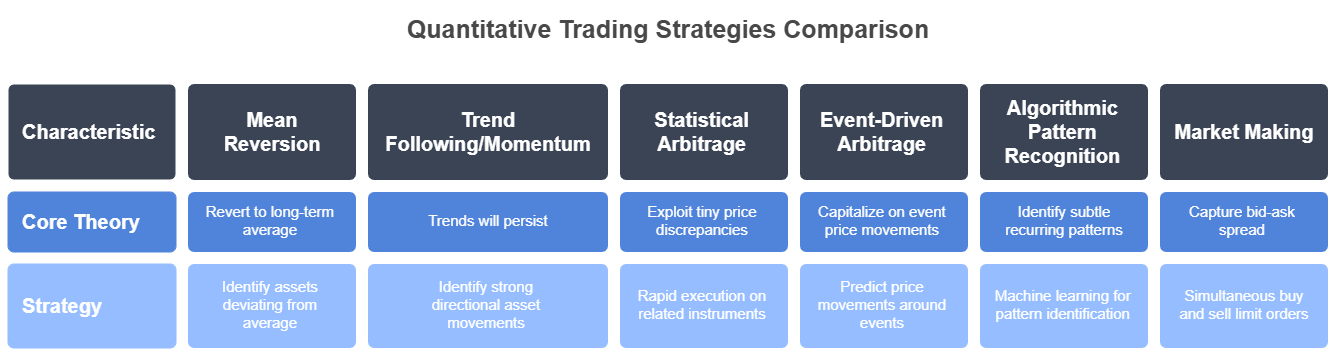
Quantitative traders use many different trading strategies. These strategies are based on different mathematical and statistical concepts. Here are a few common types of quantitative trading strategies:
- Mean Reversion: This strategy operates on the theory that asset prices and historical returns eventually revert to their long-term average.
- Trend Following / Momentum: Unlike mean reversion, these strategies bet that trends will continue. Quants create systems to identify assets moving strongly in one direction (up or down).
- Statistical Arbitrage: This involves capturing very small, often short-lived, price differences between related instruments. Traders develop these for fast trades. This often links with high-frequency trading (HFT).
- Event-Driven Arbitrage: These strategies aim to profit from price moves around big risk events. Such events include mergers, acquisitions, earnings announcements, or regulatory changes. Sometimes, even headline quant trading strategies analyze news sentiment.
- Algorithmic Pattern Recognition: This method uses machine learning or complex statistics. It looks for hidden, repeating patterns within market data.
- Market Making: This means placing buy and sell orders for an asset at the same time. The goal is to earn the small price difference, known as the spread.
These strategies are tested thoroughly with past data before use in different market conditions. They are rules-based and run systematically with the help of a quantitative trading software.
Next, let’s see what is a quant trader and what they do.
See below…
What Do Quant Traders Do?
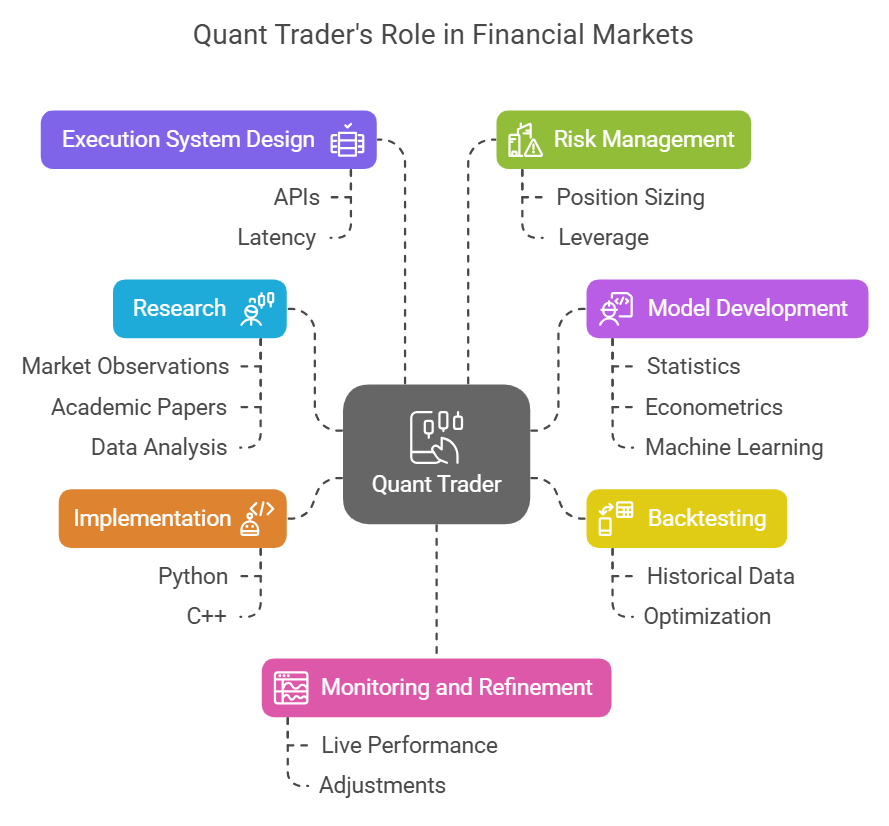
The term 'quant' itself often evokes images of complex screens and rapid-fire trading. But what do quant traders do specifically? A quantitative trader is typically involved in several stages of the trading process:
- Research: This means finding new trading ideas. Ideas can come from watching markets, reading studies, or looking at data.
- Model Development: Translating a trading idea into a precise mathematical model. This requires strong skills in statistics, econometrics, and possibly machine learning. Quantitative analysts often specialize here.
- Backtesting: This means testing the model on past market data. This key step helps check the strategy and find any weak spots or ways to improve it.
- Implementation: Quantitative developers use languages such as Python or C++ to code the strategy. Sometimes they use tools like a special quant app trader.
- Execution System Design: This is about building the system for automatic trades. The system gets signals from the model. It often links to a quantitative exchange using APIs.
- Risk Management: Defining strict rules for position sizing, leverage, stop-losses, and overall portfolio diversification. Risk management is paramount to ensure long-term viability. This falls under broader portfolio management.
- Monitoring and Refinement: This means always watching how the strategy performs live. Changes are made as needed. Markets evolve, and strategies can lose their edge.
In essence, a quant trader uses quantitative skills to design, test, implement, and manage trading strategies, leveraging technology to execute them systematically. This is the core function explaining what quant firms do.
Quant Trader vs Quant Researcher
In quant trading firms, there are two main roles. These are the quant trader vs the quant researcher. Both fit the "quants meaning," but they focus on different tasks:
- Quant Researcher: Primarily focuses on developing new trading strategies and models from scratch.
- Quant Trader: Their main job is to use, manage, and improve trading strategies. Researchers or the traders themselves might have created these strategies. Their focus is more on day-to-day profitability and execution quality.
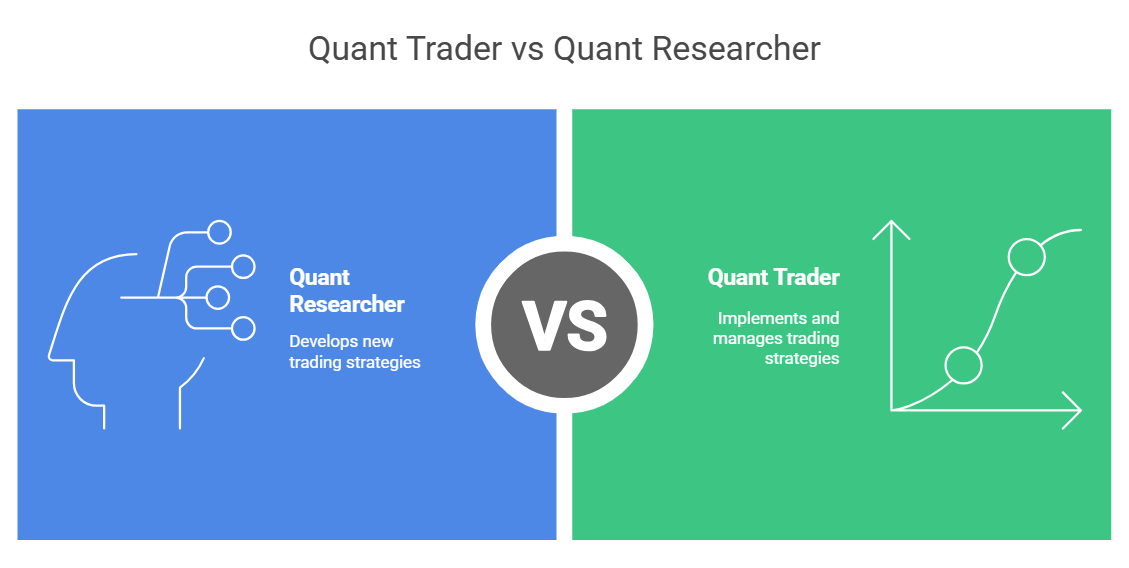
Think of researchers as the architects designing the plan. And the traders are like engineers who build and run things based on those plans.
How To Become a Quantitative Trader
Breaking into the field of quantitative trading is challenging and competitive. Want to know how to break into quant? Or how to become a quantitative trader? The usual path has a few important parts:
- Strong Quantitative Education: A bachelor's degree is often the starting point. Common fields are Math, Statistics, Physics, Computer Science, Engineering, or Economics. Many successful quants hold Master's degrees or PhDs, especially in research roles. Coursework in probability, statistics, calculus, linear algebra, and differential equations is fundamental. Understanding what a quant is in finance requires this strong base.
- Programming: Excellent programming skills are essential. Python is popular for research and data analysis. And C++ is often needed for low-latency execution systems. These are common in high-frequency trading. Knowing databases (like SQL) and statistical packages (like R or MATLAB) is helpful.
- Financial Market Understanding: You don't need to be a typical financial analyst. However, understanding how markets work is useful. Understanding different assets (like stocks or crypto) and basic finance also helps. This knowledge helps create good trading strategies.
- Data Analysis Skills: A core part of the job is handling large amounts of data. This includes doing careful statistical analysis and backtesting.
- Practical Experience: Internships offer great advantages. Good places include quant trading firms, hedge funds, or investment banks.
- Problem-Solving Mindset: Quants constantly face complex, open-ended problems. Demonstrating strong analytical and problem-solving skills is critical.
The best quant trading firms have tough interviews. These interviews test skills in math, statistics, coding, and solving problems. It’s a field that demands continuous learning and adaptation. Knowing how to get into quant means cultivating this blend of skills.
Quantitative Trading vs Algorithmic Trading
The terms quantitative trading and algorithmic trading are similar. They often overlap. However, they are not exactly the same. Understanding the quantitative trading vs algorithmic trading distinction is helpful:
- Quantitative Trading uses math and statistical models to identify trading opportunities. It’s about the why – the logic and analysis behind the trade. A strategy derived from quantitative analysis is a quantitative trading strategy.
- Algorithmic Trading refers to the method of using computer programs (algorithms) to execute trades based on pre-set instructions. It’s about the how – the automated execution of the trade.
Essentially, algorithmic trading is often the tool used to implement quantitative trading strategies. A quant trader creates a model. This is quantitative trading. Then, they often use an algorithm. This algorithm makes the trades based on the model's signals. This part is algorithmic trading.
Today's markets often need speed and precision. This is true when managing many trades. In these cases, quantitative trading nearly always uses algorithms to make the trades. The goal for both is to trade systematically and avoid the emotional pitfalls that can affect a human trader. This synergy is also prevalent in crypto quant trading. The term quantitative trading refers to this same data-driven approach.
Want to use systematic, data-based methods in Forex trading, similar to quantitative trading? Check out some of the best forex brokers in the industry: Pepperstone and FP Markets or even Deriv.


